
Glucagon/saline was administered from 0 minutes as a 2-minute intravenous bolus or as a 30-minute infusion (same total glucagon dose). On individual days, esmolol/saline was infused from -15 to 30 minutes. Methods and Results In a randomized crossover study, 10 healthy men received combinations of esmolol (1.25 mg/kg bolus+0.75 mg/kg/min infusion), glucagon (50 µg/kg), and identical volumes of saline placebo on 5 separate days in random order (saline+saline esmolol+saline esmolol+glucagon bolus saline+glucagon infusion saline+glucagon bolus). We therefore investigated hemodynamic effects and safety of high-dose glucagon with and without concomitant beta-blockade. Norepinephrine is not unreasonable but careful due to the predominantly vasoconstricting effects without inotropy, which due to increased afterload, can negatively affect cardiac output.Background Intravenous high-dose glucagon is a recommended antidote against beta-blocker poisonings, but clinical effects are unclear. Avoid Isoproterenol as this can cause peripheral vasodilation and thus hypotension avoid dobutamine alone for this same reason. Catecholamines – first line are Epinephrine or Dopamine, due to both inotropic effect and vasoconstriction. Acts to increase contractility, does not raise HR. CaCl has 3-5x more calcium than Ca gluconate, but is sclerosing to veins and hence must be given through central lines.
.jpg)
IV calcium – can give CaCl (if have central line) or Ca Gluconate (if peripheral line). Even though this is considered a 1st-line “antidote” there is actually limited data to support this. This increases contractility and possibly heart rate.
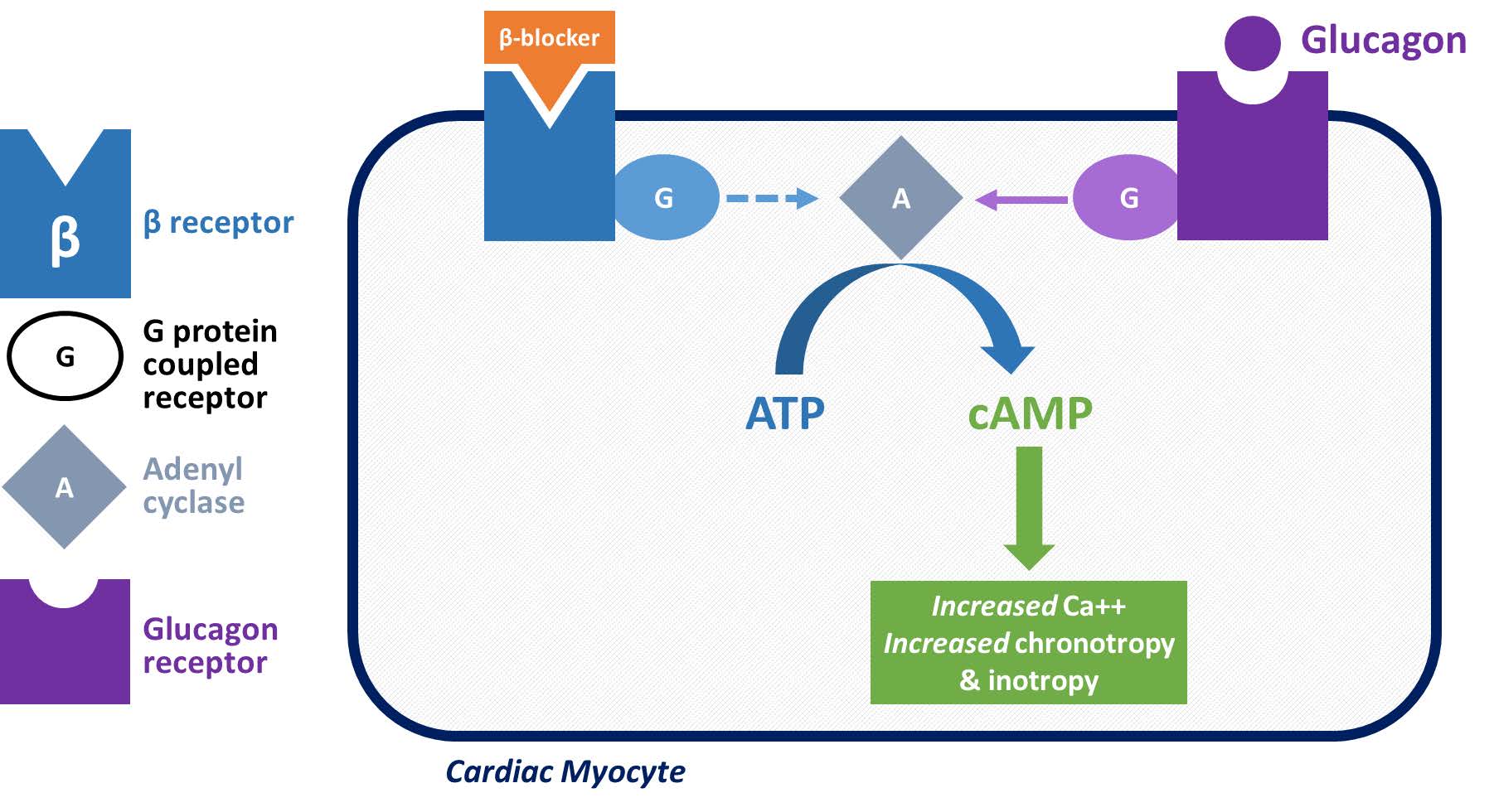
If positive response, can start an infusion at 2-5 mg/hour.Īctivates adenylate cyclase to raise cAMP levels, which increases intracellular Ca releat. Glucagon – 5 mg bolus over 1 minute, can repeat 10-15 minutes later. Side effects: Anticholinergic effects = 1) CNS effects, 2) GI – decreased saliva, nausea, vomiting, ileus, 3) GU – urinary retention, 4) CV – tachycardia (obviously) and arrhythmias, 5) Eyes – blurry visionĢ.
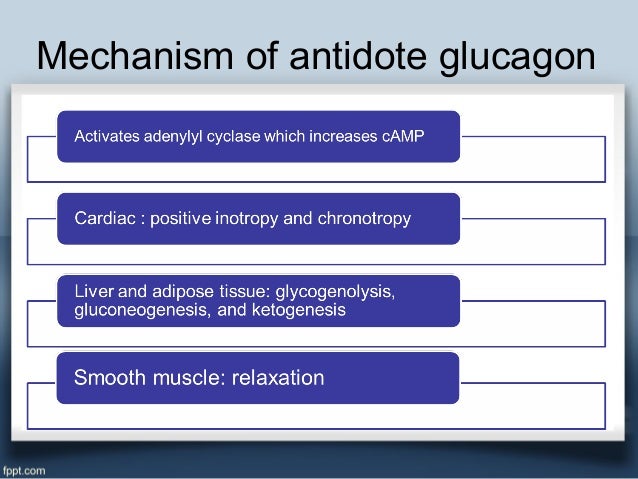
Also does not work in transplanted hearts (as they lack vagal innervation). Atropine – 0.5 mg pushes at a time, q3-5 minutes, maximum of 3 g.Īcts at the AV node – will not work for block at or below the bundle of His. Medical Therapy for Beta-Blocker Toxicity:ġ. Remember your ACLS Bradycardia Algorhithm, which emphasizes treatment for symptomatic bradycardia first with atropine (0.5 mg at a time, up to max 3 g) if ineffective, follow with transcutaneous pacing +/- infusions of dopamine or epinephrine.Can also see mild hyperkalemia and hypoglycemia.ĭdx includes overdose of calcium channel blockers, digoxin, and cholinergic agents. On EKG, can see PR prolongation leading ot AV block, and sometimes QRS prolongation (with certain beta blockers like sotalol). Clinical Manifestations: Mainly hypotension and bradycardia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
